Our Services
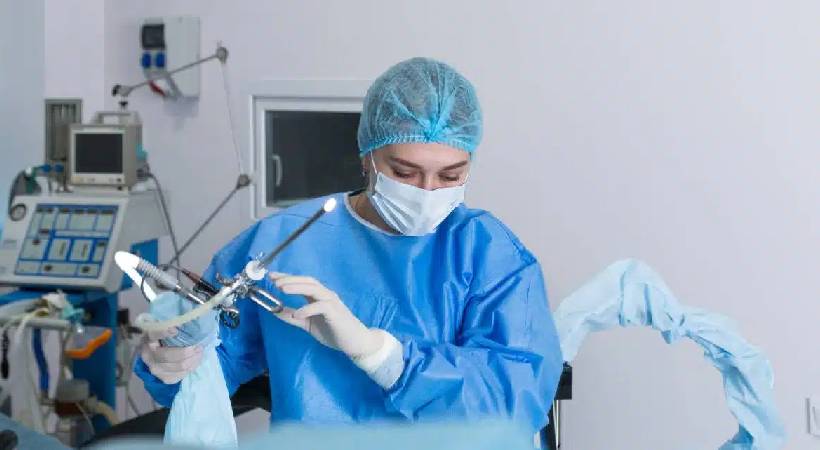
Introduction
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions inside the uterus. A thin, lighted instrument called a hysteroscope is inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterine cavity. Diagnostic hysteroscopy is used to identify abnormalities, while operative hysteroscopy allows for surgical treatment of these conditions during the same procedure. This technique is highly effective for evaluating abnormal uterine bleeding, infertility, and structural issues.
Causes for Performing Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy may be recommended to evaluate or treat the following conditions:
Diagnostic Hysteroscopy:
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Heavy, prolonged, or irregular bleeding.
- Infertility: To investigate uterine abnormalities affecting conception.
- Recurrent Pregnancy Loss: Assessing uterine shape or scarring.
- Postmenopausal Bleeding: To rule out serious conditions like cancer.
- Suspected Uterine Abnormalities: Fibroids, polyps, or congenital malformations.
Operative Hysteroscopy:
- Uterine Fibroids or Polyps: Removal of growths causing symptoms.
- Intrauterine Adhesions: Cutting scar tissue to restore normal anatomy (Asherman’s syndrome).
- Septate Uterus: Correcting congenital uterine malformations.
- Retained Products of Conception: Removing tissue following miscarriage or delivery.
- Endometrial Ablation: Treating abnormal bleeding by destroying the uterine lining.
- Foreign Body Removal: Retrieving misplaced intrauterine devices (IUDs).
Symptoms Indicating Hysteroscopy
Patients may present with symptoms requiring diagnostic or operative hysteroscopy, such as:
- Heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding.
- Unexplained infertility or recurrent miscarriages.
- Pelvic pain.
- Postmenopausal bleeding.
- Suspicion of fibroids, polyps, or structural abnormalities during imaging studies.
Diagnosis Prior to Hysteroscopy
- Medical History and Examination: Assessing symptoms and risk factors.
- Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasound: Transvaginal ultrasound to identify uterine abnormalities.
- Sonohysterography: Saline infusion ultrasound for better visualization.
- Blood Tests: To rule out other causes of symptoms (e.g., anemia, hormone levels).
Treatment: Diagnostic and Operative Hysteroscopy Procedure:
- Preparation:
- Scheduled after menstruation for optimal uterine visibility.
- Local or general anesthesia may be used, depending on the procedure’s complexity.
- Diagnostic Hysteroscopy:
- The hysteroscope is inserted through the cervix into the uterine cavity.
- The uterus is distended using saline or carbon dioxide for better visualization.
- The surgeon examines the lining and records findings.
- Operative Hysteroscopy:
- Specialized instruments are passed through the hysteroscope to perform surgery.
- Fibroids, polyps, or adhesions are removed, and structural abnormalities are corrected.
Post-Procedure Care:
- Minor cramping or spotting is common.
- Pain relief with over-the-counter medications.
- Resume normal activities within 1–2 days.
- Avoid sexual activity or tampon use for 1–2 weeks to reduce infection risk.
Benefits of Hysteroscopy
- Minimally invasive with a quick recovery time.
- Combines diagnosis and treatment in a single procedure.
- Reduces the need for major surgeries like hysterectomy.
- High success rates for treating uterine abnormalities.
Risks
- Rare Complications:
- Uterine perforation or injury to nearby organs.
- Infection or excessive bleeding.
- Fluid overload (from distension medium).
- Failure to Complete: In cases of severe cervical stenosis or uterine scarring.
Conclusion
Hysteroscopy is a safe and effective procedure for diagnosing and treating uterine conditions. It offers a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery, with minimal downtime and excellent outcomes. Women experiencing abnormal uterine bleeding, infertility, or recurrent miscarriages should discuss hysteroscopy with their gynecologist to determine if it’s the right approach for their condition.
We’d love to hear from you !
Our Gallery








Unveiling New Horizons in Fertility, One Article at a Time
Who Is at Higher Risk for Ectopic
Expert Insights by Dr. Rashmi Bhamare – 0 to 9...
Benefits of Normal Delivery: Expert Care by
Pregnancy is a beautiful journey, and choosing the right care...
First Trimester Struggles: Gentle Guidance from a
First Trimester Struggles: Expert Pregnancy Care by a Gynecologist in...
Navigating High-Risk Pregnancy: Expert Guidance and Care
Finding out your pregnancy is “high-risk” can trigger a wave...




